Crocus Sativus Linn (Iridaceae) is used widely in tropical and subtropical countries for a variety of purposes in both household and for medicinal purposes. The stigmas of the plant are used for they contain a variety of chemical constituents like the Crocetin, Crocin and other flavonoids which make them suitable to possess diversified medicinal properties for treating various ailments. In countries like India and other Asian countries, Saffron is been used in their traditional medicine from the pre?historic ages. Chemical constituents were studied for their diversified properties and this review focus on the detailed chemical constituents along with the pharmacological properties tested with the plant.
Crocus Sativus Linn is a flowering plant in the crocus family and is commonly known as saffron. It is widely used as spice and as a coloring and flavoring agent in the preparation of various foods and cosmetics. It is native to Iran and Greece. It is now cultivated largely in Southern Europe, Tibet and other countries. In India, it is mainly cultivated in Kashmir and Uttranchal. The stigmas of the plant are mainly used for therapeutic purposes. The stigmas of Crocus Sativus Linn (Saffron) are used as coloring and flavoring agents in the preparation of food in different parts of the world. Apart from its use in preparation of food, the stigmas of the plant are used for the treatment of a variety of disorders traditionally. The medicinal properties attributed to saffron are extensive.
Crocus Sativus Linn is a grass like tuber plant with purple or lilac colored flowers. The flower stalk rises from a bulb, and is a long, white, slender tube; the flower itself being large, and of a beautiful lilac color. Leaves radical, linear, dark green above, pale green below, enclosed in a membranous sheath, sometimes remaining fresh nearly the whole winter. Corolla in two segments, between which the long styles hang out. Stigmas three, large, nearly an inch long, rolled at the edges, bright orange. The stigmas of saffron are the parts that have been used in medicine. They have a pleasantly bitter and somewhat warming taste. They contain a large portion of extractive matter, and a portion of volatile oil.

The stigmas of the plant are mainly used for its medicinal properties extensively in traditional medicine for various purposes, as an aphrodisiac, antispasmodic, expectorant, for treatment of stomach ailments, reducing stomachache and for relieving tension. In Persian traditional medicine, it is used for depression. It is also used to treat insomnia and in the treatment of the measles, dysentery, jaundice, cholera etc. Topically it is applied in the form of paste to treat skin diseases like acne. It is also used in weaving industry as a dyeing agent and in the preparation of various perfumes and incense sticks.
It is considered as a tonic for heart and nervous system and for smoothing menstruation.
Charaka used the powdered stigmas as one of the drugs in the treatment of cataracts, night blindness and poor vision. Sushruta used it as a blood purifier and to treat skin eruptions internally. It is also used as an antibacterial agent, antiseptic, anti?fungal and antiflatulent traditionally.
Saffron was also used as a nervine sedative, emmenogogue, in treatment of fever, melancholia and enlargement of the liver. It is also used as analgesic, diuretic, immune stimulant, interferon inducer, and for inhibiting the thrombin formation. At low doses, it causes the stimulation of the pregnant uterus and in larger amounts it can cause constriction and spasm.
Saffron is also a protective agent against chromosomal damage, a modulator of lipid peroxidation, and an Antiseizure, for reducing blood pressure and also used in treatment of psoriasis.
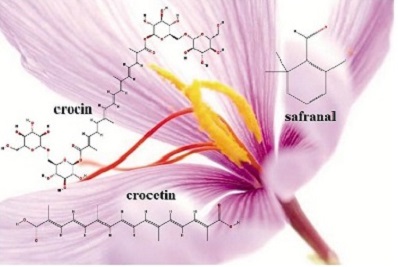
Chemical studies on Crocus Sativus stigmas reported that it possesses carotenoids like crocetin (also called α?crocetin or crocetin?I), its glycosidic forms are digentiobioside (crocin), gentiobioside, glucoside, gentioglucoside and diglucoside.
γ?Crocetin (monomethyl ester), γ ?crocetin (dimethylester), trans crocetin isomer, 13?cis?crocetin; α?carotene,β?carotene, lycopene, zeaxanthin and mangicrocin, a xanthone?carotenoid glycosidic conjugate.
The colouring components of saffron were crocins, which are unusual water?soluble carotenoids (cis and trans glucosyl esters of crocetin). The monoterpene aldehydes picrocrocin and its deglycosylated derivative safranal (dehydro?β?cyclocitral), formed in saffron during drying and storage by the hydrolysis of the picrocrocin, are also important components of saffron, responsible of its bitter flavour and aroma, respectively. Saffron’s golden yellow orange color is primarily the result of Crocin pigments. Anthocyanins, flavonoids, vitamins (especially riboflavin and thiamine), amino acids, proteins, starch, mineral matter, gums and other chemical compounds presence were also described to make their presence in Saffron. Among the constituents of saffron extract, Crocetin is mainly responsible for its pharmacological activities.

Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, India.
Received: 05 March 2011, Revised and Accepted: 08 April 2011